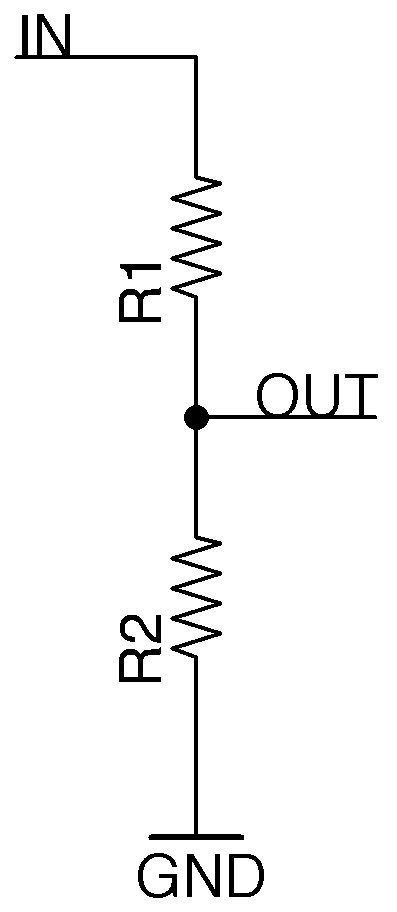
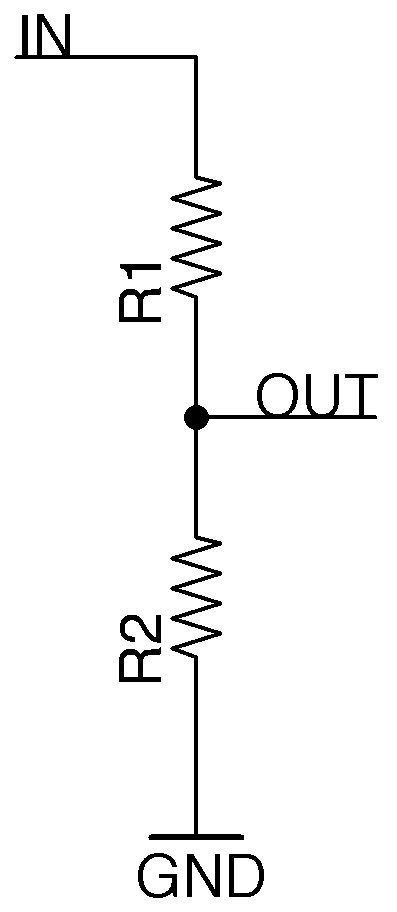
A voltage divider produces an output voltage that's a fraction of its input voltage, determined by the two resistors R1 and R2.
The output voltage is determined by \(V_o=V_i\frac{R2}{R1 + R2}\).
Resistor dividers are often used to generate reference voltages or as level shifters; their high impedance means that attempting to draw significant current from them will cause the voltage to vary.